How to Improve Your SEO on Google and Compete with the Big Boys
27/06/2018 | Digital Marketing | 15 minutesThere’s no easy way to say this…
SEO is HARD.
Only Google employees know how to make website rank, but SEOs have a good idea of what Google are looking for, and after reading this blog post, so will you.
I’m going to show you how to cover all the bases to improve your SEO and help you compete with the big boys in your industry.
On page SEO
The first place to start should be with your on page SEO, or changes you can make on your website. On page SEO encompasses all the work you do on your website to help it to rank. This includes the content on your pages, the way your website is structured and the HTML behind the scenes.
Website Content
Without a doubt the most important thing when it comes to on page SEO is content. For many of the clients we work with, one the biggest areas for improvement is their content, with much of it being “thin” and lacking any substance. Generally, the content on your website should;
- Be unique – Creating unique content can be difficult. For example, I’m sure someone, somewhere has written about on page SEO before, but it’s important to put your own slant on the content you create and be unique, or if possible, find a niche that hasn’t been explored before.
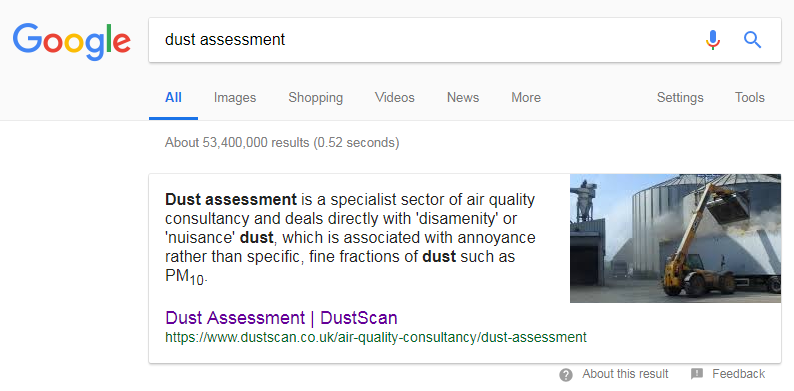
- Provide answers or solutions for users – Take a look at this blog post we created for our client Beaumont Forest. The post gets straight to the point and provides an answer to the question, whilst pushing users off to other relevant pages. The post is now the second biggest landing page on the site after the homepage. Providing answers to questions can also increase your chances of achieving a featured snippet, as achieved by our client DustScan (see below) for one of their target keywords, “dust assessment”.
- Use different types of media – Using different types of media such as videos or imagery can help to split up your content, provide a different perspective and help users to understand your point of view.
- Use keywords with search volume – Keyword research is key if you want people to find your website. There’s no point optimising your pages around keywords that no one is searching for or are too competitive to rank for. Google’s Keyword Planner Tool can give you a good idea of keyword search volume and how commercially competitive the keyword is. Beware though, it uses paid advertising data meaning it may not be as accurate for improving your organic SEO efforts.
Website Architecture
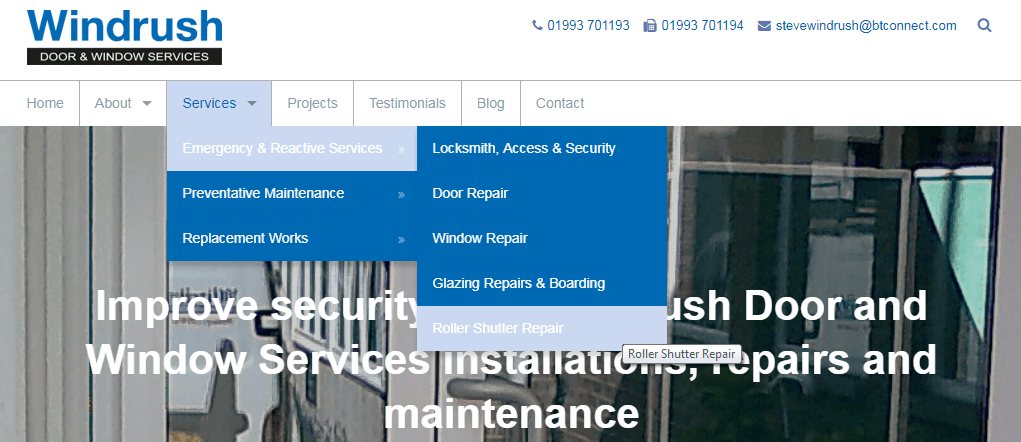
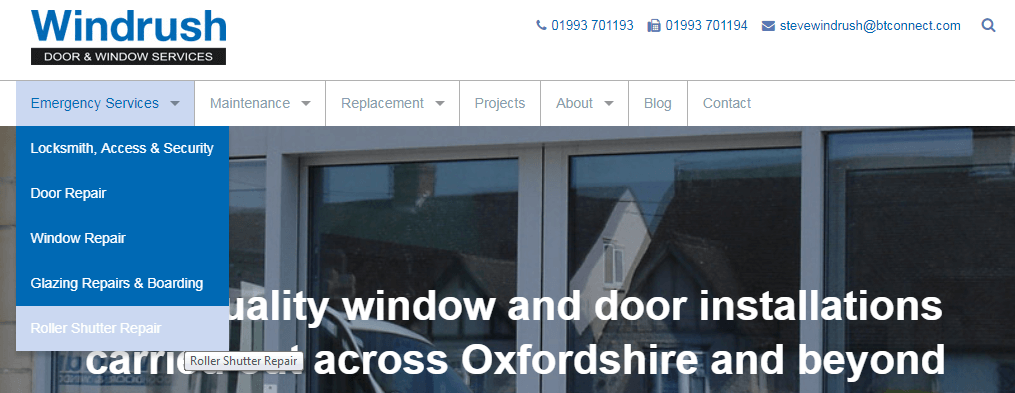
We’ve dealt with many websites who struggle to rank for their target keywords because they’re sending conflicting signals to Google. If your website is difficult for users to use, then chances are it will be difficult for Google’s robots to crawl as well. Our client, Windrush Door & Window Services, saw around 100% increase in traffic and conversions after we changed the navigation and URL structure on their website.
Old Windrush Door & Window Services Architecture
New Windrush Door & Window Services Architecture
As best practice, the architecture of your website should;
- Work efficiently on mobile devices – Around 50% of your traffic is likely to come from mobile devices, so this medium shouldn’t be neglected. You can check how your website performs on mobile by using Google’s Mobile Friendliness Tool .
- Load quickly – It’s crucial that your website loads quickly, especially on mobile devices where users are likely to be utilising slower mobile network speeds. You can check how fast your website loads using Google Pagespeed Insights .
- Have no issues with duplicate content – Duplicate content can be an issue for many websites, especially on ecommerce websites where there are similar product variations that are hard to distinguish.
- Use keyword focused URLs – Just as it’s important to use keywords in your content, it’s also important to use keywords in your URLs so users know they will be landing on a relevant page when they click through to your website.
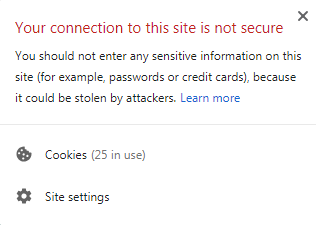 Use a secure (HTTPs) connection – In 2014, Google’s algorithm changed to favour secure (HTTPs) websites over unsecure (HTTP) websites. Since then this has become more and more ingrained in Google’s core algorithm. If your website isn’t using a HTTPs connection then your search engine rankings might suffer and your users might be greeted by an unsightly message about the website not being secure.
Use a secure (HTTPs) connection – In 2014, Google’s algorithm changed to favour secure (HTTPs) websites over unsecure (HTTP) websites. Since then this has become more and more ingrained in Google’s core algorithm. If your website isn’t using a HTTPs connection then your search engine rankings might suffer and your users might be greeted by an unsightly message about the website not being secure.
Website Code (HTML)
Hidden behind the visible content on the page is HTML; the code base that enables browsers to render your website. When Google crawls the HTML on your website it’s looking at the following;
- Meta title – The meta title is one of the most important elements on your page when it comes to on page SEO. It’s the title that’s seen on the SERP (Search Engine Results Page) and is how Google determines what content on your page is about. It’s important to use your target keyword here both for users and for Google.
- Meta description – Although not directly used in Google’s ranking algorithm, the meta description still plays a very important part in getting users to your website. It’s what appears below the meta title on the SERP and should give more details about what the page is about. It should be written to encourage users to click through to your site.
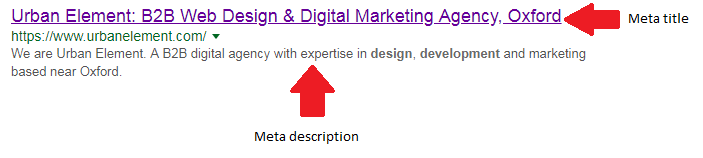
- Structured data – Structured data provides extra information to search engines about certain elements on your page. For example, many ecommerce websites markup the ratings on their products so that the star rating appears on Google search. Like the meta description, this can also be useful for enticing click through.
- Heading tags – Your heading tags, such as your H1, are still used in Google’s ranking algorithm but aren’t always considered as important as the meta title. The heading tags, particularly the H1, should contain information to let the user know they are on the right page, and if it makes sense, the keyword focus of that page.
Off page SEO
Off page SEO refers to any factors outside of your website that contribute to the ranking of your website. This includes how trusted your website is, how many quality backlinks there are to your website, how relevant the website might be to a particular user and your reputation on social media.
Website Trust
People use brands they trust and the same applies online. After all, Google wants to remain a trusted source of information in itself. Google uses a number of factors to establish how trusted a website is, including;
- Bounces – Nothing to do with trampolines, unfortunately. Google measures whether a user bounces (click the back button) quickly after reaching the page. It uses this data to determine whether the user had a good experience on the site. For example, if a user navigates to a website and leaves straight away then it’s likely the site didn’t meet their expectations, potentially meaning that website will be ranked lower in the future.
- The long click – Similar to bounces, a long click occurs when a user visits a search result and didn’t return, meaning that they landed on a page that met their needs.
- Domain age – Many businesses highlight their experience in the industry, including Urban Element! It’s the same online. A domain that has a trusted history on the internet is more likely to be trusted in the future. However, a new domain that doesn’t have this history will need to gain trust over time.
- Manual action penalties – If your website has been flagged for violating Google’s Webmaster Guidelines then you may receive a manual action penalty from Google which will cause your rankings to plummet. You can see if you’ve been given a manual action penalty in the Manual Actions Report in Google Search Console.
Backlinks
Backlinks are like word of mouth on the web. If you’re receiving a backlink from another website then, in most cases, it means your website is reputable and worth visiting. Google also recognises this and uses backlinks as a ranking factor. But what makes a backlink good or bad?
Good backlinks…
- Are from trusted, quality, respected sites
- Use anchor text related to the page content
Bad backlinks…
- Have been purchased to manipulate search engines
- Are spammed all over the web in irrelevant locations
You can find out more about how backlinks apply to Google’s algorithm and how to analyse backlinks in this blog post.
Personal
You may notice that websites you visit frequently appear at the top of the search results. That’s not a coincidence, Google uses cookies to monitor your search behaviour and show you search results that you’ve visited before. Your location is also monitored, providing you give permission, meaning that Google can show you results from your local area.
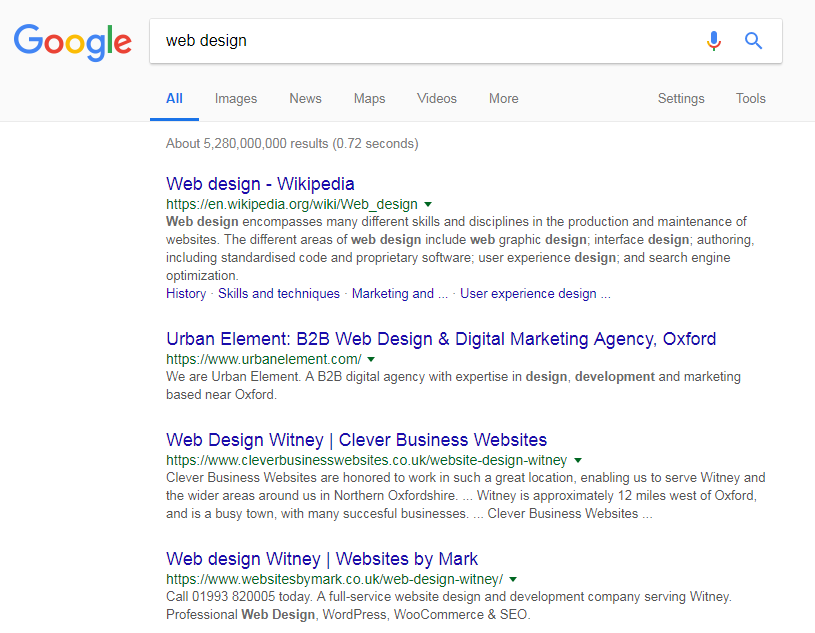
For example, a search for “web design” from our office in Witney returns this result.
On the other hand, a search for “web design” from central Glasgow returns this result.
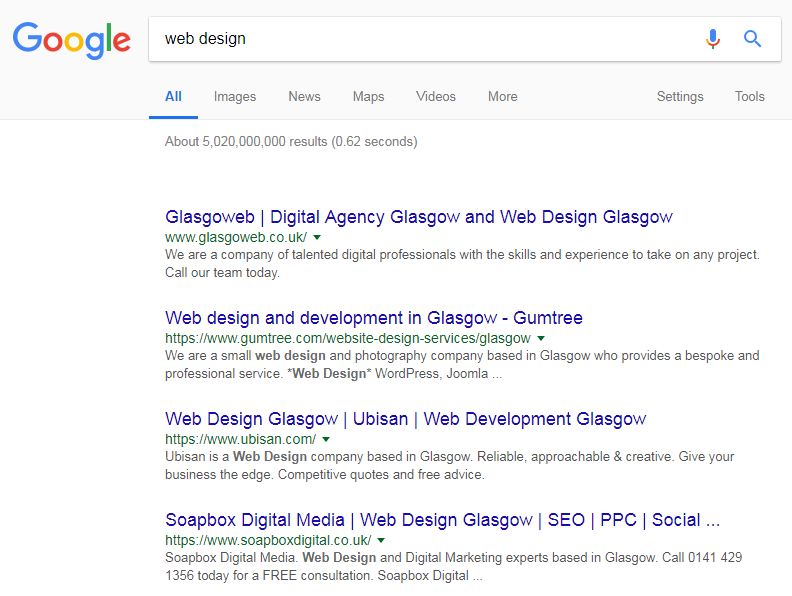
As you can see, the same search term is used each time, but the results depending on the location of the searcher are very different.
Social Media
Although not directly related to search engine rankings, social signals can give search engines an indication as to whether your website should be trusted or not. These signals are predominantly based around how many social shares your website content has and who these shares are from. This could be anything from retweets on Twitter to shares on Facebook.
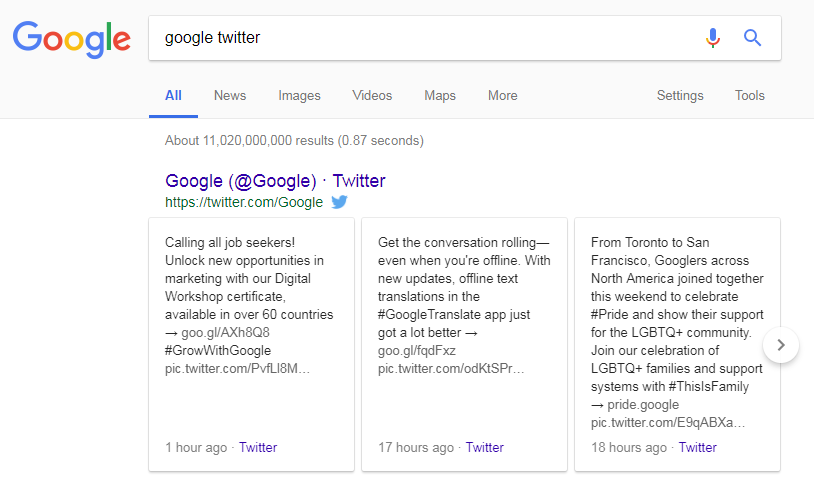
The evidence for social media having bearing on SEO is limited, but some studies have concluded that the two are undoubtedly linked . It would be naive to disagree as the world of social media is growing and can give Google reliable indicators of brand trust from things like reviews. Twitter even have carousels (see image below) that often appear at the top of Google’s search results, making this prime real estate for SEOs.
What next?
If you’ve laid these foundations then you should stand a good chance of being ranked highly by Google. If you need help or ongoing support then contact Urban Element and we’ll give you a helping hand.


