Understanding User Intent and Its Impact on SEO
21/02/2019 | Digital Marketing | 10 minutesAt its inception, the developers behind Google Search likely had understanding user intent at the bottom of their list of priorities. Today, Google Search is a more complex beast, designed to go beyond keywords and establish the intention behind a particular search query.
What do we mean by user intent?
Google refers to user intent as a goal that you’re trying to accomplish by typing or speaking a query. Let’s say you’re looking for an SEO agency near your location. To find this you may use a search query like “seo”, but…
- Do you want to know about the SEO discipline?
- Maybe you’re interested in SEO services?
- Are you looking for a local SEO company or a national one?
It’s not clear what you’re looking for with this search query, so in this instance Google will return a mixed bag of results.
However, if you’re more specific you make your intent much clearer to Google. A search query like “seo agency near me” would return much more relevant results (see below).
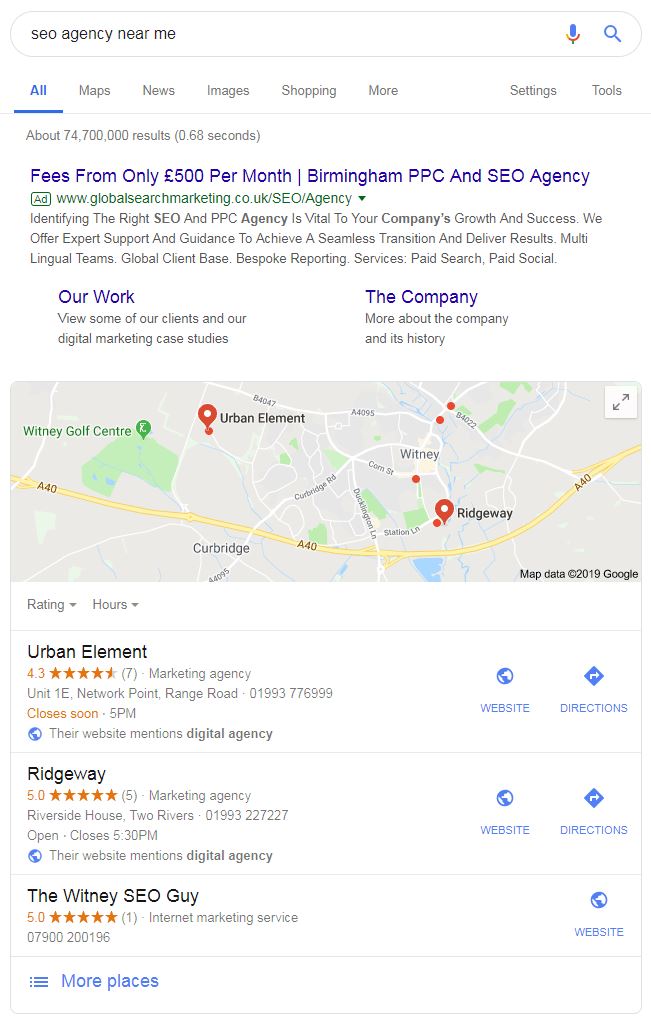
How does Google understand user intent?
Hummingbird
Google honed in on user intent in a big way in 2013. The year saw the launch of Google’s Hummingbird algorithm. The update focused on how humans use natural language to search Google and how this language should be interpreted to display the most relevant search results.
RankBrain
In 2015, Google once again focused its efforts on user intent, with the launch of machine learning algorithm update, RankBrain. Like Hummingbird, RankBrain focused on the use of natural language, whilst learning over time about what users are looking for from particular search queries.
Google Search Quality Raters
Then there’s the human element. Google hires over 10,000 search quality raters to manually evaluate search results following 200 pages of strict guidelines. The data gathered from these ratings is fed back into Google’s algorithm, improving search engine results pages over time.
The different types of Google search query
Before optimising your pages for certain keywords, think about what users are looking for when they use a particular search query. Google outlines 4 different types of search query…
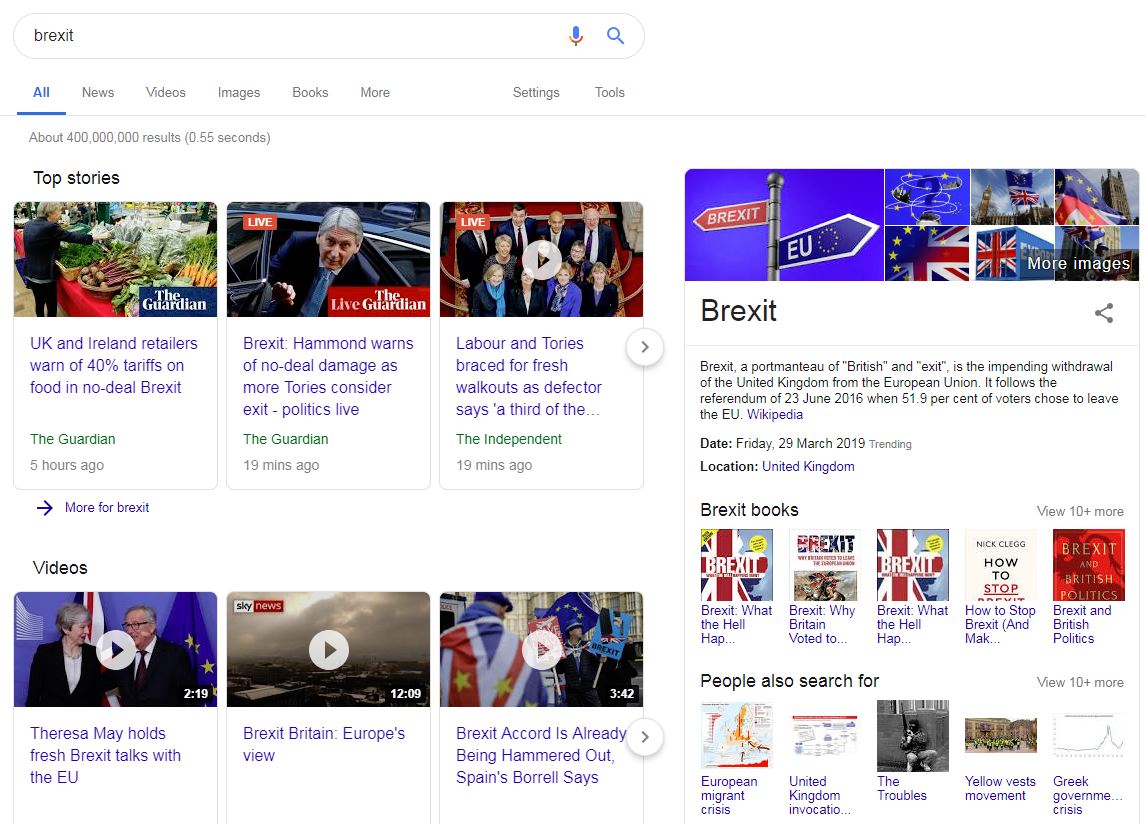
- A know query indicates the intent of finding information about a topic. A search such as “brexit” would indicate that users want information on the UK exiting the EU, which isn’t a simple topic. Sometimes users want a simple answer. These type of queries are known as know simple queries. An example of this would be “who is the prime minister?”, which would return a very specific result.
- A do query indicates the intent of fulfilling a goal. In other words, users want to do something. Verbs such as “get” and “buy” are prime examples of do query prefixes.
- A website query indicates that a user is looking for a particular website e.g. “urban element”.
- A visit-in-person query indicates just that. A user is looking to find a particular place to visit in person. These queries are often used by mobile users looking to find something nearby. For example, a user looking to find an Indian restaurant to eat at might use the query “indian restaurant”.
How does this impact SEO?
Simply put, you should be focusing on your users. They are the lifeblood of your website, just as they’re the lifeblood of Google Search. To optimise your website to match user intent be mindful of the SERP that is triggered by your keywords. Don’t over optimise, take pointers from high ranking pages and deliver an experience that helps your users achieve their goals.


